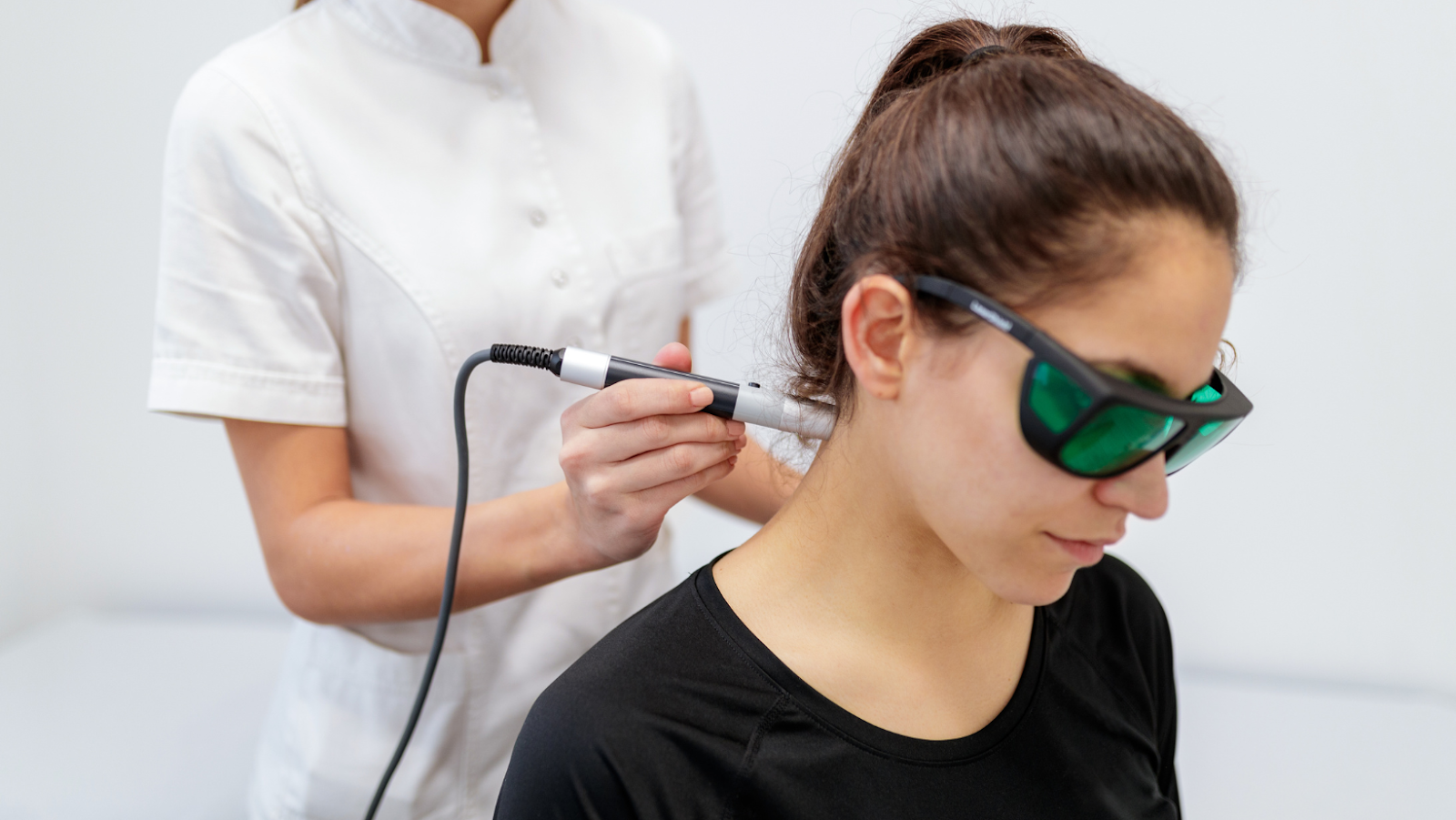
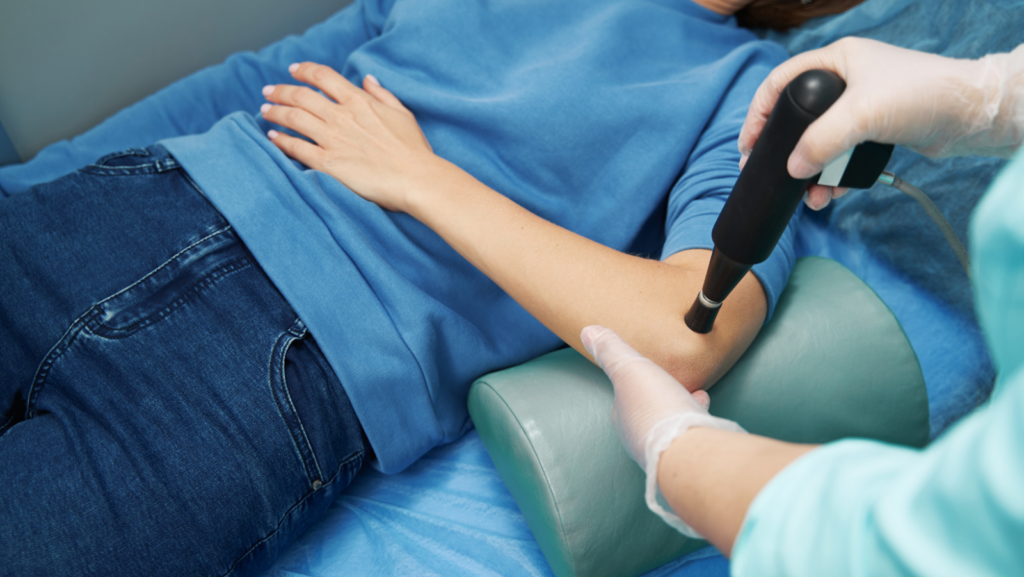
Shock therapy for muscles, also known as neuromuscular stimulation, is a therapeutic technique that involves using electrical or cold stimuli to target and stimulate muscles. These therapies are designed to improve muscle function, alleviate pain, and aid recovery. It’s an innovative approach to addressing various muscle-related issues, but understanding its nuances is crucial for effective use.
The use of shock therapy for muscles has a history dating back centuries. In ancient Greece, athletes used electric fish to stimulate their muscles for enhanced performance. In recent times, technological advancements have led to the development of modern electric muscle stimulation (EMS) and Cryotherapy. Today, shock therapy has evolved into a diverse field with applications ranging from physical therapy to sports performance enhancement.
Understanding Muscles
To grasp the significance of shock therapy for muscles, it’s essential to understand how muscles function. Muscles are the body’s workhorses, responsible for movement, stability, and posture. They contract and relax in response to nerve signals, and maintaining their health is vital for overall well-being.
Muscles can face various issues, such as strains, spasms, and soreness due to overuse or injury. These issues can hamper daily activities and athletic performance. Shock therapy offers a promising solution to address these problems effectively.
Types of Shock Therapy
When it comes to shock therapy for muscles, there are two primary approaches: Electric Muscle Stimulation (EMS) and Cryotherapy. Each has its unique mechanisms and applications.
Electric Muscle Stimulation (EMS)
EMS involves the application of electrical impulses to specific muscles or muscle groups through electrodes placed on the skin. These impulses mimic the body’s natural signals, causing the muscles to contract and relax. This process can enhance muscle strength, improve circulation, and alleviate pain.
EMS has many applications, from rehabilitation and physical therapy to enhancing athletic performance. It can be used to target specific muscle groups, aiding in muscle recovery and development. Athletes often incorporate EMS into their training routines to supplement traditional strength training.
Cryotherapy
Cryotherapy, on the other hand, focuses on using cold temperatures to treat muscles. This therapy typically involves exposure to extremely cold air or applying cold packs to the affected areas. The cold stimulus reduces inflammation, numbs pain, and promotes healing.
Cryotherapy is renowned for reducing muscle soreness and inflammation after strenuous activities. Athletes and individuals dealing with muscle injuries often turn to Cryotherapy to expedite recovery. Additionally, it can improve circulation and promote overall well-being.
Benefits of Shock Therapy
One of the most significant advantages of shock therapy for muscles is its ability to accelerate muscle recovery. Whether it’s through EMS or Cryotherapy, these techniques help reduce inflammation, relieve pain, and enhance blood flow, enabling muscles to heal more rapidly after injury or intense workouts.
For athletes and fitness enthusiasts, shock therapy can be a game-changer. By incorporating these techniques into their routines, individuals can experience enhanced muscle strength, endurance, and performance. It’s a valuable tool for those striving to achieve their fitness goals.
Risks and Considerations
Safety Precautions
While shock therapy for muscles holds substantial promise, safety must remain paramount. The use of EMS devices or participation in cryotherapy sessions should be conducted under the guidance of trained professionals. Incorrect usage can lead to skin irritation, muscle damage, or other complications.
Contraindications
Shock therapy is not a one-size-fits-all solution. Individuals with certain medical conditions, such as those relying on pacemakers, those with epilepsy, or those with cold intolerance, should exercise caution or even avoid these treatments altogether. Consulting with a healthcare professional before embarking on shock therapy is a prudent step to ensure safety and appropriateness based on individual circumstances.
Comparing Shock Therapy Methods
EMS vs. Cryotherapy
In the world of shock therapy for muscle treatment and recovery, there’s an ongoing debate between two powerful methodologies: Electric Muscle Stimulation (EMS) and Cryotherapy. EMS involves applying electrical impulses to muscles via electrodes on the skin, mimicking natural muscle contractions. On the other hand, Cryotherapy focuses on using cold exposure to reduce inflammation and promote healing.
To illustrate the comparison, consider an athlete recovering from an intense workout. EMS can target specific muscle groups, helping with muscle recovery and development. Cryotherapy, meanwhile, may alleviate muscle soreness and inflammation. The choice between the two depends on the individual’s situation and needs.
Effectiveness Metrics
Determining the effectiveness of shock therapy methods is a crucial aspect of the decision-making process. To gauge the true impact of EMS and Cryotherapy, it’s essential to examine relevant metrics, such as their ability to improve muscle recovery, reduce pain, and enhance overall performance. These metrics provide valuable insights into the practical benefits of each method.
The Science Behind Shock Therapy
Neural Adaptations
The efficacy of shock therapy is deeply rooted in its influence on neural adaptations. In the case of EMS, the electrical impulses directly engage motor neurons, promoting muscle contractions. This process is pivotal in improving muscle strength and endurance.
To delve deeper, consider an individual using EMS for muscle rehabilitation. EMS helps recruit muscle fibers that may have been dormant due to injury, facilitating the rebuilding of neural pathways and ultimately leading to improved muscle function.
Physiological Changes
Beyond neural adaptations, shock therapy induces various physiological changes in the body. For instance, Cryotherapy’s application of cold can constrict blood vessels, reduce inflammation, and alleviate pain. Understanding these changes provides insight into the broader benefits of these therapies.
If we examine Cryotherapy’s physiological effects, it’s evident that the reduction in inflammation not only aids in muscle recovery but also contributes to overall well-being. This process mimics the body’s natural response to injury, promoting healing at an accelerated rate.
Addressing Myths and Misinformation
When it comes to shock therapy, myths and misconceptions can be prevalent, often deterring potential beneficiaries. It’s essential to identify and dispel these misconceptions to provide clarity and ensure informed decisions. One common belief is that shock therapy is only for professional athletes. In reality, these therapies have applications for people of all fitness levels and backgrounds, and they can address various muscle-related issues, not just those experienced by elite athletes.
To combat myths and misinformation effectively, reliance on evidence-based insights is paramount. By examining scientific studies, clinical trials, and real-world experiences, we can substantiate the claims made about the benefits of shock therapy methods.
Summary of Key Findings
Our comprehensive exploration of shock therapy for muscles has illuminated the potential for enhancing muscle health, recovery, and performance. By comparing Electric Muscle Stimulation (EMS) and Cryotherapy, understanding the underlying science, and dispelling common myths, we have provided readers with a holistic perspective. This knowledge equips individuals to make informed decisions tailored to their specific needs and goals.
Whether you’re an athlete seeking peak performance, recovering from an injury, or simply looking to improve your muscle well-being, shock therapy offers a promising avenue. Embracing these innovative methods can be a transformative step toward optimizing your muscle health and overall vitality.