Internal scar tissues, also known as adhesions, are fibrous bands that form between tissues and organs within the body due to injury, surgery, or inflammation. While often invisible to the naked eye, their impact on skin health and overall well-being can be profound. Beyond the surface, these adhesions can hinder movement, disrupt organ function, and even contribute to chronic pain.
Impact on Skin Health
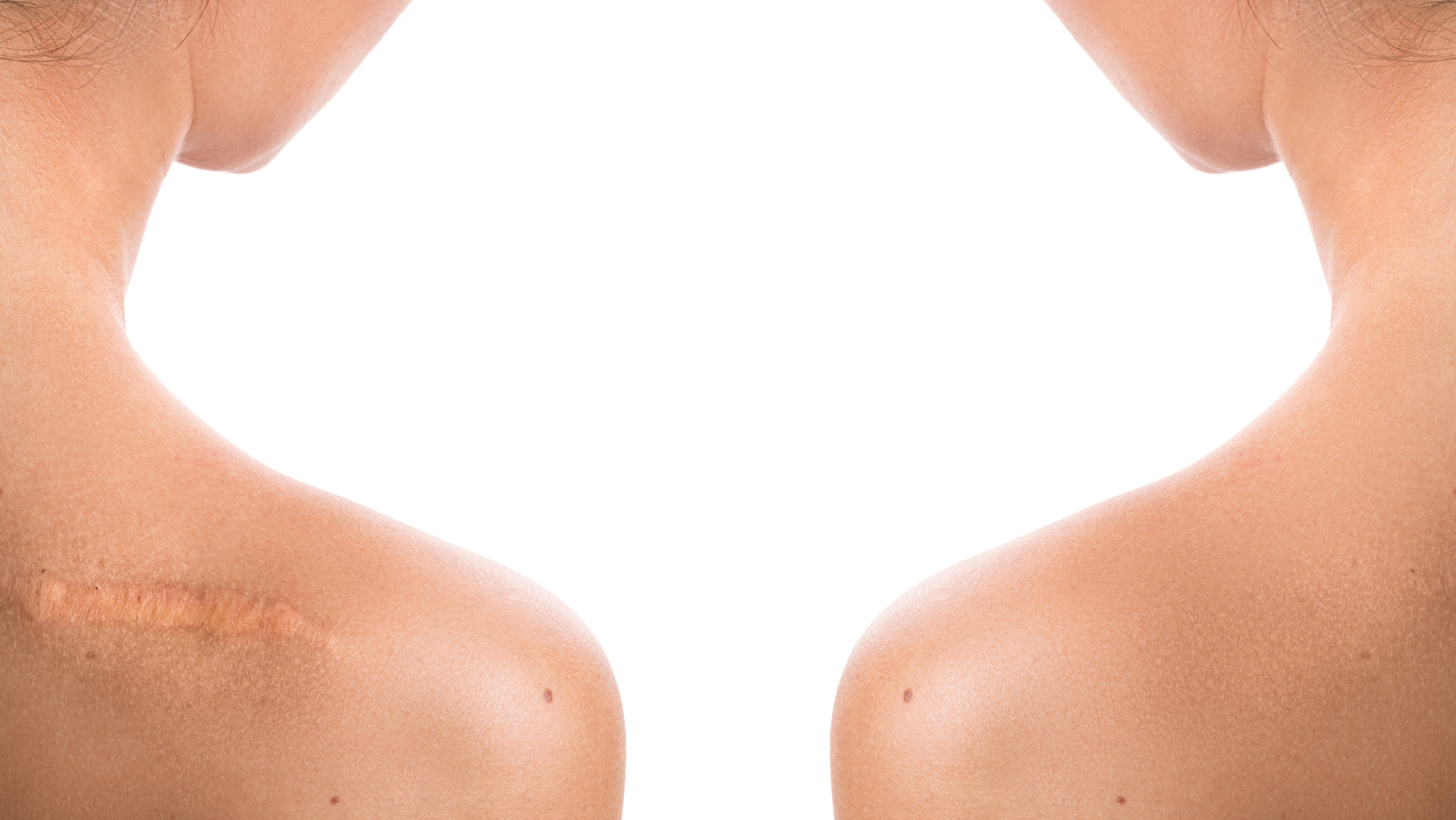
Internal scar tissues can disrupt blood flow, hinder collagen cells production, and impede wound healing, leading to uneven skin tone, reduced elasticity, and increased susceptibility to conditions like acne and eczema. Nicotine restricts blood flow, exacerbating these effects by further limiting the delivery of oxygen and nutrients to the skin tissues. Collagen cells, essential for healthy skin elasticity and strength, are adversely affected by the presence of internal scar tissues. Addressing these adhesions is crucial for restoring skin vitality and promoting optimal healing from within, while also considering the health of surrounding skin.
Understanding Internal Scar Formation
Internal scar formation can occur for various reasons, each leaving a distinct mark within the body. Causes of internal scarring encompass a spectrum of events, including surgical procedures where tissue is intentionally disrupted, traumatic injuries that prompt the body’s healing response, and inflammatory conditions that result in tissue damage and subsequent repair.
The scar tissue permanent line, representing the boundary between healed and unhealed tissue, is a crucial aspect of internal scar formation, including surgical scarring. It delineates the area where new collagen fibers are deposited during the healing process, marking the site of past injury or trauma.
Causes of Internal Scarring
- Surgical Procedures: Surgeries, whether minor or significant, often involve incisions into bodily tissues, triggering the body’s wound healing mechanisms, which may lead to scar tissue formation.
- Trauma and Injuries: Sudden, forceful impacts or accidents can cause internal damage to organs or tissues, initiating the body’s repair processes and potentially resulting in the formation of scar tissue as part of the healing response.
- Inflammatory Conditions: Chronic inflammatory conditions like arthritis or inflammatory bowel disease can lead to ongoing tissue damage and repair cycles, fostering the development of internal scars over time. Addressing chronic inflammation is paramount in managing and mitigating the formation of internal scars, highlighting the importance of comprehensive treatment strategies that target both the underlying inflammation and its resultant scar tissue formation.
Types of Internal Scar Tissues
Scar tissue develops in various forms, each presenting unique characteristics and implications for health and function within the body. Collagen fibers, crucial components of connective tissue, play a central role in the formation and structure of internal scars. Adhesions, keloids, and contractures all involve the deposition and organization of collagen fibers during the healing process.
Types of Internal Scar Tissues
- Adhesions: Adhesions are bands of scar tissue that form between internal organs or tissues, often as a result of surgical incision or inflammation These adhesions can cause organs to become stuck together, potentially leading to pain, discomfort, or complications. Blood vessels, integral components of tissue repair, contribute to the formation of adhesions by supplying nutrients and oxygen to support the healing process and increase blood flow.
- Keloid Scars: Keloids are raised, overgrown scars that extend beyond the boundaries of the original wound. They can develop internally, affecting deeper tissues, and may result from surgical incisions, trauma, or inflammatory processes.
- Contractures: Contractures occur when scar tissue forms over a joint, restricting its movement and flexibility. Internal contractures can develop following surgeries or injuries involving joints, impairing mobility and causing functional limitations, often causing pain. Understanding the types and causes of internal scar tissues is crucial for managing their impact on overall health and well-being.
Signs and Symptoms
Identifying signs and symptoms is crucial for early detection and management of various conditions, especially considering potential differences in how they manifest on darker skin tones.
From subtle behavioral changes to pronounced physical discomfort, recognizing these indicators empowers individuals to seek timely treatment and support. Minor itching, often accompanying scar tissue formation, can serve as a subtle yet significant signal of the body’s healing process and its response to internal changes.
Physical Indications
Physical indications offer tangible clues about one’s health, ranging from changes in appearance to bodily functions. From persistent coughs to mobility issues, paying attention to these cues helps in assessing and addressing underlying health conditions effectively, especially those related to the affected area or injured tissue.
Emotional Impact
Health challenges evoke a wide range of emotions, including fear, sadness, and resilience. Acknowledging and addressing these emotions is vital for holistic well-being, fostering resilience, and promoting mental health amid adversity.
Access to mental health resources and support systems is essential for navigating the emotional impact of health conditions. Integrating scar massage techniques into self-care practices can also have a positive impact on emotional well-being by promoting relaxation and reducing stress levels.
Medical Assessment
A thorough medical assessment is essential for accurate diagnoses and treatment plans. It involves evaluating a patient’s medical history, symptoms, vital signs, and past records to understand their health status and tailor care accordingly.
Consultation with Healthcare Professionals
Consulting with healthcare professionals allows patients to engage with experts, discuss concerns, and develop personalized care plans. These interactions foster open communication and collaboration between patients and their healthcare team.
Diagnostic Procedures
Diagnostic procedures like imaging tests (X-rays, CT scans, MRI, ultrasound) and biopsies play a crucial role in identifying medical conditions. They enable clinicians to visualize internal structures and analyze tissue samples, guiding treatment decisions and improving patient outcomes.
Imaging Tests
Imaging tests, including X-rays, MRI, CT scans, and ultrasounds, provide detailed views of internal body structures. They aid in diagnosing conditions like fractures, tumors, and organ abnormalities, helping healthcare professionals plan treatment effectively.
Biopsy
Biopsy involves extracting tissue samples for microscopic examination, often to detect cancer, assess organ function, or identify infections. Various techniques, such as needle and surgical biopsies, are used based on the target area. Results guide treatment decisions and enable tailored care plans for patients.
Conservative Approaches
Scar management is a vital aspect of conservative approaches, prioritizing non-invasive treatments for healing and symptom relief, while avoiding surgical procedures for injured tissues. Within this framework, two notable methods are:
Hands-On Manual Therapy
Physical therapists play a pivotal role in administering hands-on manual therapy, another valuable approach within conservative therapy. Skilled manipulation of soft tissues and joints by physical therapists aims to alleviate pain and enhance mobility, addressing internal scar tissue while promoting the health of surrounding healthy tissue.
Techniques like massage and mobilization, guided by physical therapists, aim to restore balance and promote self-repair, including scar tissue massage.
Sole Supports
Sole Supports offers custom orthotics to address foot-related issues, optimizing foot function and reducing strain on the body, potentially benefiting those with internal scar tissue while supporting the health of surrounding healthy tissue. Tailored to individual anatomy and gait, they improve stability and mobility for better overall biomechanical efficiency.
Advanced Treatment Options
These cutting-edge modalities offer promising avenues for patients seeking effective remedies beyond traditional approaches, including scar tissue removal and skin grafts. Among these innovative solutions are:
EPAT (Extracorporeal Pulse Activation Technology)
EPAT, or shockwave therapy, uses acoustic pressure waves to enhance blood circulation and speed up healing for conditions like plantar fasciitis and tendinopathies, offering a non-invasive alternative to surgery with minimal downtime.
ESWT (Extracorporeal Shockwave Treatment)
ESWT delivers high-energy shockwaves to target areas, stimulating tissue repair and improving conditions such as tendonitis and stress fractures, providing a non-surgical solution for pain relief and mobility improvement.
EMTT (Extracorporeal Magnetotransduction Therapy)
EMTT utilizes magnetic fields to promote tissue healing and reduce inflammation, making it beneficial for chronic musculoskeletal issues and joint diseases, offering a safe, non-invasive treatment option.
Instrument Assisted Soft Tissue Mobilization (IASTM)
IASTM employs handheld instruments to break down adhesions and scar tissue, improving the range of motion and reducing pain for conditions like myofascial pain syndrome and tendonitis, enhancing overall functional recovery.
How to Get Rid of Internal Scar Tissues
Laser therapy, a rapidly evolving treatment modality, utilizes focused light energy to target specific tissues, aiding in scar remodeling and promoting healing. By stimulating collagen production and reducing inflammation, laser therapy offers a non-invasive option for managing internal scar tissues and improving skin health.
With its precise targeting and minimal downtime, laser therapy emerges as a valuable addition to the repertoire of advanced treatment options for internal scar tissues, including massaging scar tissue.
In addition to these advanced treatment options, individuals can explore various methods to help alleviate internal scar tissues. Consultation with healthcare professionals is essential to determine the most suitable approach based on individual circumstances and health status.
Lifestyle Modifications
In scar healing, lifestyle adjustments like regular exercise, stress management, and sufficient rest can aid recovery, including from internal scar tissue.
Additionally, incorporating scar tissue treatment methods into one’s daily routine, such as targeted exercises and self-massage, can contribute to breaking down adhesions and fostering a more flexible and resilient internal environment.
Nutrition for Scar Healing
Vitamin E oil is a valuable addition to scar healing regimens. It can be topically applied to scars to moisturize the skin, reduce inflammation, and improve their appearance.
Alongside foods rich in vitamins C and E, zinc, protein, and omega-3 fatty acids, incorporating vitamin E oil into your routine nourishes the body and supports smoother healing.
Importance of Hydration
Hydration is vital for scar healing. Water supports skin elasticity, nutrient transportation, and overall tissue repair. By staying properly hydrated through regular water intake and hydrating foods, individuals can optimize the healing process and promote healthier, less noticeable scars.
Conclusion
Addressing internal scar tissues requires a comprehensive approach encompassing physical and emotional well-being. Understanding the causes and types of internal scarring is crucial for tailored treatment plans. Conservative methods like manual therapy and advanced treatments such as EPAT and ESWT offer promising avenues for healing.
Lifestyle adjustments, including nutrition and hydration, support the body’s natural healing processes. By combining medical expertise with personal diligence, individuals can embark on journeys toward holistic recovery, fostering resilience and restoring vitality from within.