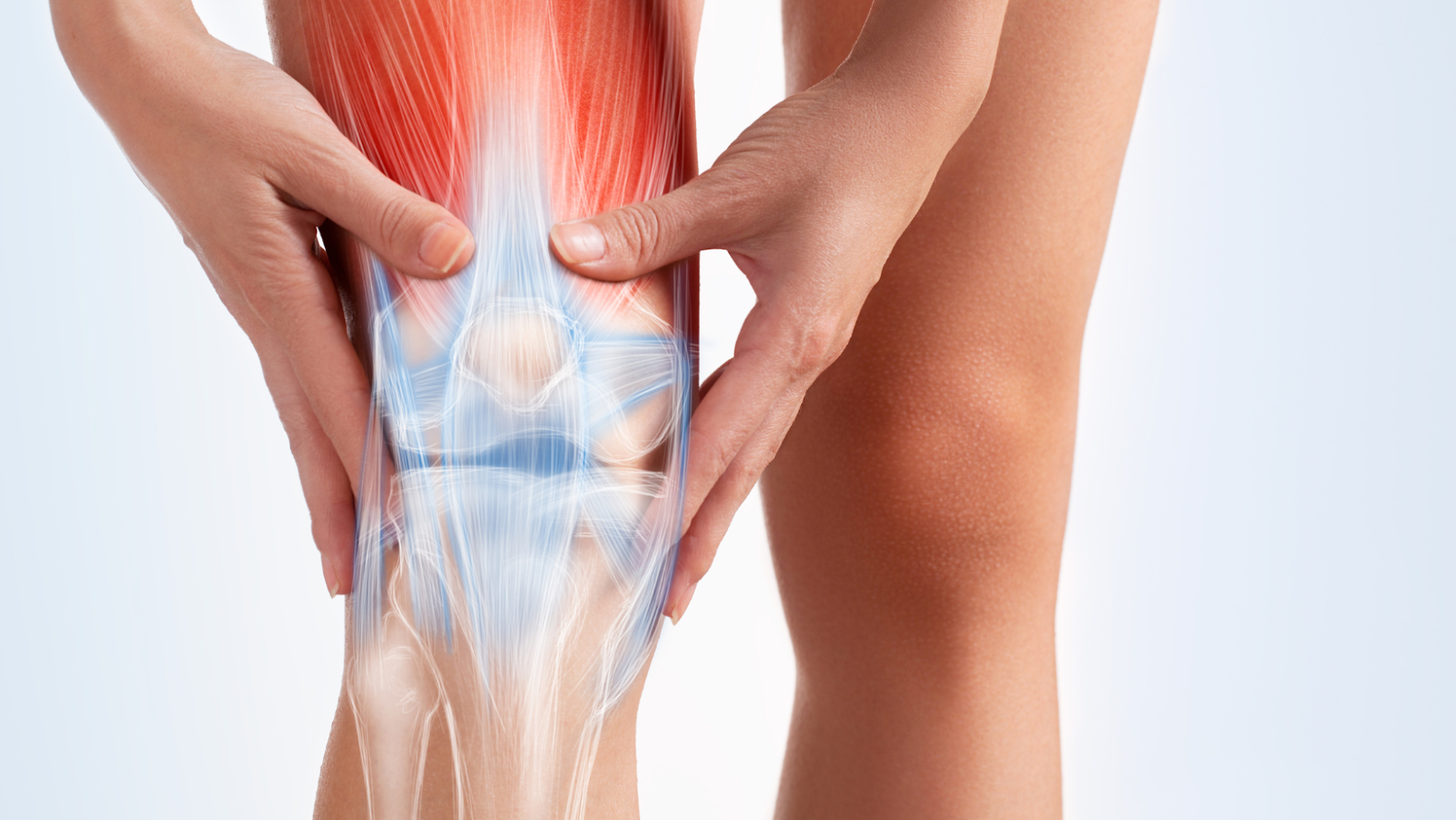
Muscle adhesions, often shrouded in mystery, are a common aspect of muscular health. These adhesions are fibrous bands or tissues that develop between muscle layers or around muscles, causing them to stick together. To better understand how to address muscle adhesions, it’s essential to delve into their definition and basic characteristics.
Muscle adhesions may seem inconspicuous, but their impact on muscular health should not be underestimated. These adhesions can restrict the natural range of motion, reduce flexibility, and impede muscle function. Additionally, they can contribute to chronic pain and muscle imbalances and even decrease athletic performance. To maintain optimal muscular health, it’s crucial to appreciate the significance of addressing and preventing muscle adhesions.
Understanding Muscle Adhesions
Before delving into the formation process, types, causes, and risk factors of muscle adhesions, it’s essential to have a fundamental understanding of what they are and how they affect the body.
Formation Process
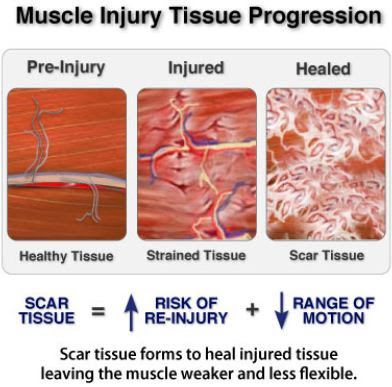
Muscle adhesions develop through a complex process involving muscle fibers, connective tissues, and inflammation responses. When muscle fibers are subjected to excessive stress or injury, the body initiates a healing response that can inadvertently lead to adhesions. These adhesions form as collagen fibers bind together, creating bands of tissue that limit muscle movement.
Types and Classification
Muscle adhesions can manifest in various ways, and understanding their types and classification is essential for effective treatment and prevention.
Surface Adhesions
Surface adhesions occur between layers of muscle fibers or between muscles and surrounding connective tissues. They can be responsible for localized pain and discomfort, making movements less fluid.
Deep Adhesions
Deep adhesions are more complex and form within the muscle itself. These can be particularly problematic, as they can restrict blood flow and hinder the overall function of the muscle. They often require specialized treatment.
Causes and Risk Factors
Several factors contribute to the development of muscle adhesions. Understanding these causes and risk factors can help individuals take proactive steps to prevent them.
Overuse and Repetitive Movements
Engaging in repetitive activities or overusing specific muscle groups can lead to the development of muscle adhesions. Athletes and individuals in physically demanding professions may be particularly susceptible.
Trauma and Injuries
Acute injuries, such as muscle strains, can trigger the formation of adhesions during the body’s healing process. Proper rehabilitation and care are crucial to prevent their development.
Poor Posture and Ergonomics
Prolonged periods of poor posture or ergonomically unfavorable work environments can contribute to the formation of muscle adhesions. Maintaining good posture and ergonomic practices can play a role in their prevention.
Symptoms of Muscle Adhesions
Muscle adhesions can manifest with various symptoms, ranging from mild to severe, depending on their location and extent. One of the most common symptoms associated with muscle adhesions is pain and discomfort. Individuals may experience localized or referred pain in the affected area. This discomfort can range from a dull ache to sharp, stabbing pain, often worsening with movement or pressure.
Muscle adhesions can also significantly limit the natural range of motion in affected muscles and joints. This restriction can make simple tasks like reaching, bending, or lifting objects challenging. Reduced flexibility can also increase the risk of injury.
Furthermore, as muscle adhesions hinder normal muscle function, they can have a considerable impact on daily activities. Simple actions like walking, climbing stairs, or sitting comfortably may become difficult or painful. In severe cases, muscle adhesions can disrupt a person’s quality of life and independence.
Diagnosis Techniques
Diagnosing muscle adhesions is a crucial step towards effective treatment. Healthcare professionals employ various techniques to confirm the presence and extent of adhesions.
Physical Examination
A skilled healthcare provider can often detect muscle adhesions through a thorough physical examination. They may palpate the affected area, assess a range of motion, and inquire about symptoms. This initial evaluation provides valuable information for diagnosis and treatment planning.
Imaging Tests
Sometimes, healthcare providers may use imaging tests to visualize muscle adhesions more clearly. Two common imaging modalities include Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) scans, which can provide detailed images of soft tissues, making them a valuable tool for identifying muscle adhesions. MRI can help determine the extent of adhesion formation and assist in treatment planning.
Ultrasound imaging, on the other hand, uses sound waves to create real-time images of the body’s internal structures. It can be used to visualize adhesions, assess blood flow, and guide diagnostic and therapeutic procedures.
Prevention Strategies
Preventing muscle adhesions is essential for maintaining optimal muscular health and preventing discomfort or injury. Incorporating these strategies into your routine can help reduce the risk of adhesion formation:
Proper Warm-Up and Stretching
Before engaging in physical activity or exercise, it’s crucial to warm up your muscles and perform dynamic stretching exercises. This helps increase blood flow and prepares your muscles for exercise demands, reducing the risk of adhesions.
Adequate Hydration
Staying well-hydrated is essential for overall muscle health. Dehydration can increase the likelihood of muscle cramps and strains, leading to adhesions. Ensure you drink enough water throughout the day, especially during exercise.
Ergonomic Practices
Maintaining good posture and practicing ergonomic techniques in your daily activities can prevent muscle imbalances and reduce the risk of developing adhesions. Whether at work or home, create ergonomic environments that support proper body alignment.
Treatment Options for Muscle Adhesions
When addressing muscle adhesions, several treatment options are available, each tailored to the individual’s condition and needs.
Physical therapy is a pivotal component of adhesion management. Skilled physical therapists design personalized exercise programs to stretch and strengthen muscles, enhance flexibility, and break down adhesions. Manual techniques, including myofascial release, are often integrated to target specific areas of adhesion.
Another effective approach involves massage therapy, where pressure is applied to relieve tension, alleviate pain, and break down adhesions, promoting relaxation and improved circulation. In some cases, healthcare providers may prescribe pain medications such as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or muscle relaxants for short-term relief. However, these should be used under medical supervision.
Emerging Therapies for Muscle Adhesions
As medical research and technology advance, new and innovative therapies for addressing muscle adhesions are emerging, offering promising alternatives to traditional treatments. Technology-based solutions include high-intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU) and extracorporeal shockwave therapy (ESWT), which are non-invasive techniques utilizing focused energy to break down adhesions and stimulate tissue healing.
Additionally, researchers are exploring novel approaches like regenerative medicine and stem cell therapy. These therapies promote tissue repair and regeneration, potentially offering long-lasting relief for individuals with severe adhesions. While traditional treatments remain effective options for managing muscle adhesions, these innovative therapies represent exciting possibilities for the future of adhesion care. Treatment decisions should always be made in consultation with a healthcare professional, considering the individual’s condition and preferences.
Summary
Understanding muscle adhesions is crucial for maintaining optimal muscular health and well-being. This comprehensive guide has delved into the definition, formation process, types, causes, and risk factors of muscle adhesions, shedding light on addressing and preventing them. Recognizing the symptoms and exploring diagnostic techniques can aid in early intervention and effective treatment.
Moreover, a range of treatment options, from physical therapy to innovative emerging therapies, offers hope for individuals seeking relief from the discomfort and restrictions caused by muscle adhesions.
By adopting prevention strategies and staying informed about the latest advancements in adhesion care, individuals can take proactive steps towards healthier muscles and a better quality of life.