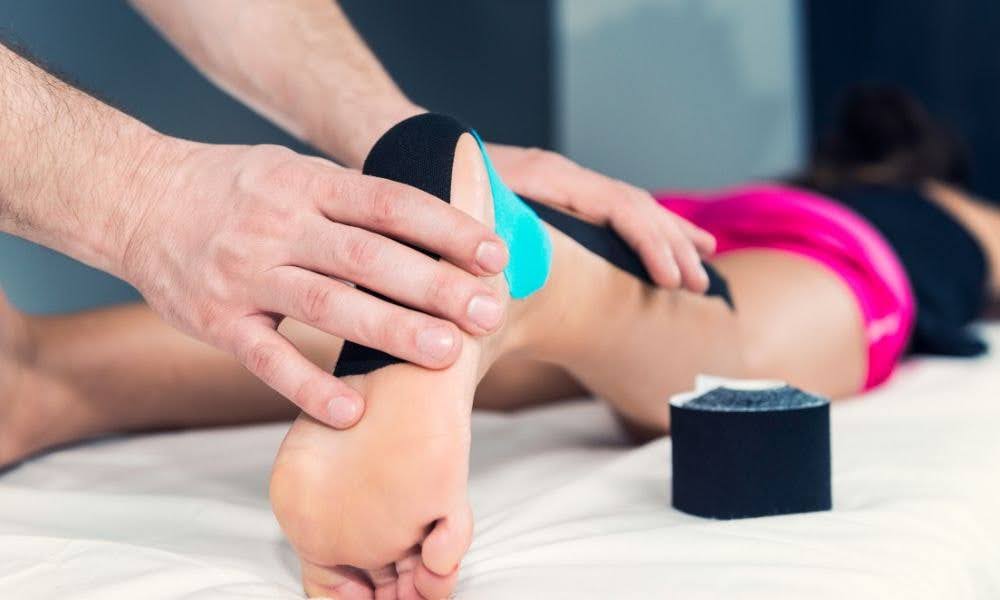
When you think about the healing process, it’s easy to imagine your body seamlessly knitting itself back together, but sometimes, that healing can create its own challenges. Scar tissue develops as your body’s natural response to injury, but unlike healthy tissue, it can sometimes lead to stiffness, discomfort, and even scar tissue pain.
Whether you’ve undergone surgery, sustained an injury, or had a deep cut, the formation of scar tissue is your body’s way of protecting and healing the damaged area. Scar tissue forms when the body produces a dense collection of collagen fibers to repair damaged tissues. While this is a vital part of the healing process, the resulting scar tissue can be less flexible than healthy tissue, leading to tightness and pain.
Over time, untreated scar tissue can interfere with your daily activities, making it important to address it through various methods, including scar tissue massage and targeted exercises.
Importance of Breaking Down Scar Tissue
Breaking down scar tissue is not just a physical necessity; it’s a step towards reclaiming your body’s functionality and comfort. When left untreated, scar tissue can harden and become a permanent barrier to physical movement and health. Actively working to remodel scar tissue through physical therapy, exercises, and massages helps ensure that newly healed tissues regain their flexibility and function.
Health Benefits
The physical benefits of addressing internal scar tissue are profound. Improved mobility tops the list, as breaking down scar tissue allows joints and muscles to move more freely. This increased range of motion directly contributes to reduced pain, often resulting from scar tissue’s tight, restrictive nature.
Furthermore, actively working to break down scar tissue enhances the healing process, allowing damaged tissue to recover and regain strength more effectively. Techniques like scar tissue massage performed by physical therapists can significantly aid in this aspect of recovery.
Psychological Benefits
Psychologically, taking proactive steps to address scar tissue can increase confidence. This comes from regaining physical abilities and experiencing less discomfort during daily activities. Additionally, improving the condition of scar tissue contributes to an overall enhanced quality of life. With fewer physical limitations and discomforts, individuals enjoy greater well-being and are more active, leading to a healthier and more fulfilling lifestyle.
Types of Scar Tissue
Understanding the different types of scar tissue is essential for determining the most effective treatment and exercise strategies. Scar tissue can vary significantly in appearance, texture, and impact on your body, making it important to recognize these variations.
Hypertrophic Scars
Hypertrophic scars are raised, red scars that form within the boundaries of the original wound. These scars result from an overproduction of collagen during healing and can be uncomfortable, often restricting movement. Massaging scar tissue in these cases, along with targeted exercises, can help break down the fibrous tissue and improve flexibility.
Keloid Scars
Keloid scars are similar to hypertrophic scars but extend beyond the original injury site. These thick, raised scars often result from an exaggerated healing response and can cause discomfort or itchiness. While a physical therapist might recommend gentle exercises and soft tissue treatments, more aggressive options such as injections or laser therapy are sometimes required for effective management.
Contracture Scars
Contracture scars occur when the skin tightens and pulls together during healing, frequently after burns or severe injuries. These scars can severely limit mobility, particularly if they form near joints. A physical therapist may recommend a combination of stretching exercises and massaging scar tissue to help improve the range of motion.
Adhesion Scars
Adhesion scars develop internally, causing tissues that should remain separate to bind together, typically after surgery or deep injuries. This type of scar can lead to significant pain and movement restrictions. Treating adhesion scars often involves specialized soft tissue techniques, such as myofascial release, along with exercises that promote flexibility and reduce pain.
Non-Invasive Exercises to Break Down Scar Tissue
Engaging in noninvasive exercises is a pivotal strategy for managing and reducing scar tissue. These exercises enhance flexibility and strength in the affected areas. They promote healing by improving blood flow and breaking up the fibrous tissue that scar tissue creates, thus aiding in pain reduction and mobility restoration.
Stretching Exercises
Stretching exercises are essential for maintaining flexibility and preventing the stiffening effects of scar tissue. Static stretching exercises like the hamstring stretch, quadriceps stretch, and shoulder stretch gently elongate the muscles and soft tissues, helping to alleviate tightness. Dynamic stretching exercises, including arm circles, leg swings, and torso twists, involve active movements that improve blood circulation and flexibility, which is crucial for maintaining a range of motion around scarred areas.
Foam Rolling
Foam rolling is a self-myofascial release technique that effectively targets and breaks down scar tissue. Benefits of foam rolling for scar tissue include increased blood flow to the area and the breakdown of the tight, fibrous tissue layers. Techniques such as the IT band roll, calf roll, and back roll focus on specific areas prone to stiffness and adhesion, promoting healing and increasing elasticity in the soft tissues.
Yoga Poses
Yoga offers tremendous benefits for managing scar tissue, such as enhancing flexibility, reducing pain, and improving overall physical and mental well-being. Effective yoga poses like Downward Dog, Cat-Cow Stretch, and Child’s Pose target multiple muscle groups, support gentle stretching of scar tissues, and encourage a healthy range of motion.
Resistance Band Exercises
Resistance bands are another excellent non-invasive way to manage scar tissue. The advantages of using resistance bands include targeted muscle strengthening and improved flexibility, which are vital for breaking down scar tissue. Key exercises like resistance band pull-aparts, leg presses with bands, and shoulder external rotations apply consistent tension to muscles and connective tissues, promoting strength without putting excessive strain on the scarred areas.
Advanced Techniques for Scar Tissue Breakdown
Advanced techniques can provide targeted and intensive treatments beyond basic exercises for those looking to enhance their scar management strategies. These methods focus on deeply affecting the scarred area to promote healing and restoration of normal healthy tissue.
Manual Therapy
- Myofascial Release: This technique involves applying gentle, sustained pressure into the myofascial connective tissue to reduce pain and restore motion, effectively breaking up developed scar tissue.
- Deep Tissue Massage: Targets deeper layers of muscle and connective tissue, helping to break up scar tissue and increase blood flow to the area, which aids in healing.
- Trigger Point Therapy: Focuses on specific areas of tight muscle fibers that can form in your muscles after injuries or overuse, helping to alleviate the tension through isolated pressure and release.
Specialized Equipment
Specialized equipment like Theragun or massage guns uses percussive therapy to deeply massage affected areas, helping to break up developed scar tissue and increase circulation. It is important to use these tools intermittently, allowing the muscles to relax between sessions to prevent overstimulation. The Graston technique involves specialized stainless steel instruments that gently scrape over the skin, enhancing the mobility of soft tissue and effectively breaking up scar tissue. Trained professionals should perform this method to ensure safety and effectiveness.
Hydrotherapy Techniques
Hydrotherapy employs water’s therapeutic properties to aid in healing and pain relief. Techniques such as contrast baths stimulate blood flow and reduce inflammation in scarred tissues, while aquatic exercises performed in a pool use water’s buoyancy to reduce stress on the body and its resistance to strengthen muscles and break up scar tissue. These techniques improve circulation and relax muscles, enhancing the overall healing process.

Exercise Routines for Specific Areas
Targeted exercise routines are vital for addressing scar tissue in specific body areas, ensuring each region receives the appropriate treatment to enhance mobility and reduce discomfort.
Upper Body
Pendulum exercises and wall climbs are effective for shoulder scar tissue. Pendulum exercises help gently mobilize the shoulder joint, while wall climbs encourage a broader range of motion, stretching and strengthening the surrounding muscles. For the elbow and arm, bicep curls and tricep extensions can improve flexibility and strength, reducing the stiffness of scar tissue.
Lower Body
Quad sets and heel slides benefit knee scar tissue by targeting the muscles around the knee, supporting joint stability and mobility. Exercises like ankle circles and toe raises are ideal for addressing scar tissue in the ankle and foot, helping to maintain or improve movement in these complex joint areas.
Core and Back
Abdominal scar tissue can be managed with pelvic tilts and abdominal bracing, strengthening the core muscles and supporting overall spine health. The Cat-Cow Stretch and Superman Exercise are beneficial for back scar tissue. These exercises increase spinal flexibility and strength, essential for managing back scar tissue and aiding overall back health.
Post-Exercise Care
After exercises aimed at breaking down scar tissue, it’s essential to care for your body to maximize benefits and aid recovery. Cooling down helps reduce heart rate gradually and prevents stiffness by encouraging muscle recovery and improving flexibility. Simple cool-down techniques include gentle stretching and slow walking, helping the body return to normal.
After exercising, it’s important to stay hydrated and eat nutritious foods to help your muscles recover. This means drinking plenty of water and eating balanced meals that include protein and carbohydrates to reduce muscle soreness.
Preventing Scar Tissue Formation
To minimize excessive scar tissue, start with immediate care after an injury. Moving early and gently helps keep flexibility and encourages proper blood flow to the injured area, reducing the likelihood of stiff scar tissue forming. Proper wound care is straightforward but essential: keep the injury clean and protected to reduce infection risk and promote healing. Physical therapy guides safe exercises to keep the injured area mobile without overstressing it, aiding in maintaining normal function and appearance. This approach speeds up recovery and helps prevent long-term issues with scar tissue.
Long-Term Gains from Scar Tissue Exercises
Think of scar tissue like a knot in a shoelace; with the right approach, it can be loosened and smoothed out. Breaking down scar tissue through dedicated exercises and treatments not only enhances your physical flexibility and comfort but also promotes long-term health and mobility. The benefits of these efforts extend well beyond the visible improvements.
Staying consistent with your exercises and patient with your progress is key. Recovery doesn’t happen overnight, and the journey might feel slow at times. However, each small step contributes to a larger change, improving how you move and feel each day. Keep at it, and you’ll notice these changes not just in your physical health but in your overall quality of life. Stay encouraged and patient; your dedication to managing scar tissue is a significant investment in your long-term well-being.